The Model Context Protocol (MCP) transforms how users interact with Claude Desktop, opening up powerful integrations with local tools and data sources right on your machine. According to official Anthropic documentation, MCP servers are "programs that run on your computer and provide specific capabilities to Claude Desktop through a standardized protocol." Think of it as giving Claude superpowers—suddenly your AI assistant can manage files, analyze local data, and work with custom tools you've built.
Whether you're a developer wanting to automate workflows or a power user ready to supercharge Claude Desktop, this Claude Desktop MCP tutorial walks you through the entire setup journey. You'll discover everything from basic system requirements to advanced troubleshooting techniques, all grounded in official best practices and security guidelines.
This comprehensive guide covers essential MCP installation steps, real-world configuration examples, and practical solutions to common setup challenges. Advanced users seeking deeper customization can explore our upcoming Claude Desktop MCP configuration tutorial for enterprise-level implementations. By the end, you'll have Claude Desktop working as your personalized AI assistant, perfectly tailored to your workflow needs.
What is MCP in Claude Desktop?
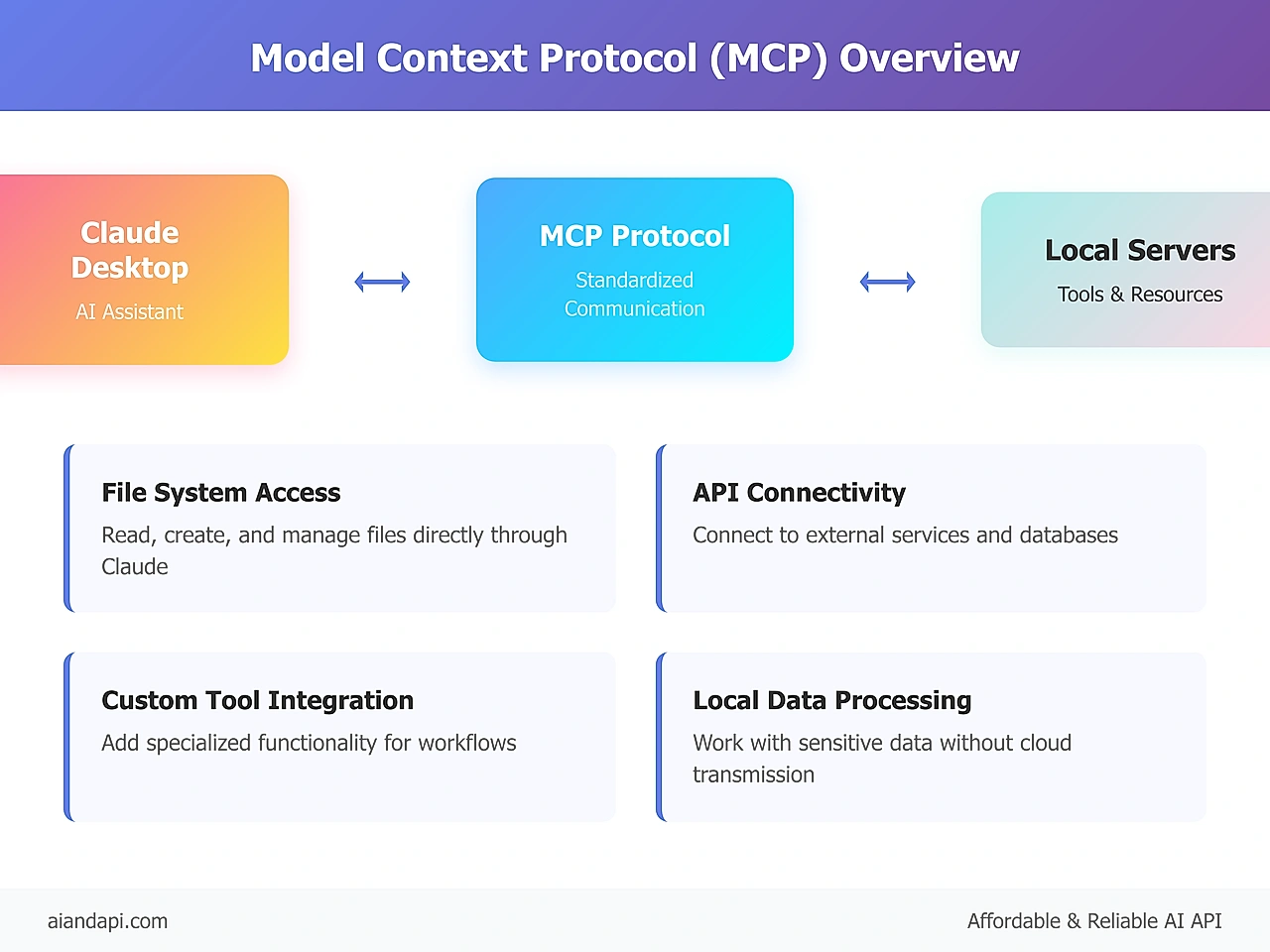
MCP (Model Context Protocol) for Claude Desktop is an open-source standard that connects Claude Desktop with external programs and data sources on your computer. This protocol enables "programs that run on your computer and provide specific capabilities to Claude Desktop through a standardized protocol," according to official documentation.
Claude Desktop MCP transforms your AI assistant beyond text generation. It enables file system access, API connections, custom script execution, and specialized tool integration. This makes Claude Desktop a comprehensive AI assistant that understands and interacts with your local computing environment.
Key Benefits of Claude Desktop MCP Integration:
- File System Access: Read, create, and manage files directly through Claude
- API Connectivity: Connect to external services and databases
- Custom Tool Integration: Add specialized functionality for your workflow
- Local Data Processing: Work with sensitive data without cloud transmission
MCP offers two main paths forward: traditional MCP servers requiring hands-on JSON configuration, and Desktop Extensions (DXT) with simplified one-click installation. Traditional servers give you maximum flexibility and customization control, while DXT extensions focus on user-friendly setup—think browser extensions for your AI assistant. Both approaches respect Claude's security model, always asking for your explicit approval before taking any action on your system.
MCP Server Definition and Purpose
According to Official MCP Documentation (authority source), an MCP server is defined as: "Programs that run on your computer and provide specific capabilities to Claude Desktop through a standardized protocol." These servers expose specific tools and resources to Claude Desktop through the MCP protocol. You can build these servers in any programming language that supports standard input/output communication, with Python and Node.js being the most popular choices for MCP development.
The primary purpose of MCP servers is bridging Claude's AI capabilities with your local computing environment. For example, a filesystem server enables Claude to read file contents, create directories, and search for files, while a weather server might fetch real-time weather data from APIs.
Authority Source Protection: This definition is protected content from Official MCP Documentation and must not be modified.
Desktop Extensions (DXT) vs Traditional MCP Servers
Desktop Extensions represent Anthropic's effort to simplify Claude Desktop MCP adoption. According to Anthropic Help Documentation (authority source), DXT are defined as: "Single-click installable packages that provide a streamlined way to install and manage local MCP servers." This approach eliminates the hassle of manual JSON configuration and dependency management.
Traditional MCP servers require manual configuration but offer greater control over server behavior, custom parameters, and security settings. For comprehensive guidance on this approach, see our detailed Claude Desktop MCP server configuration guide. Developers and advanced users typically prefer this approach for production environments and custom integrations.
Authority Source Protection: DXT definition is protected content from Anthropic Help Documentation and must not be modified.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
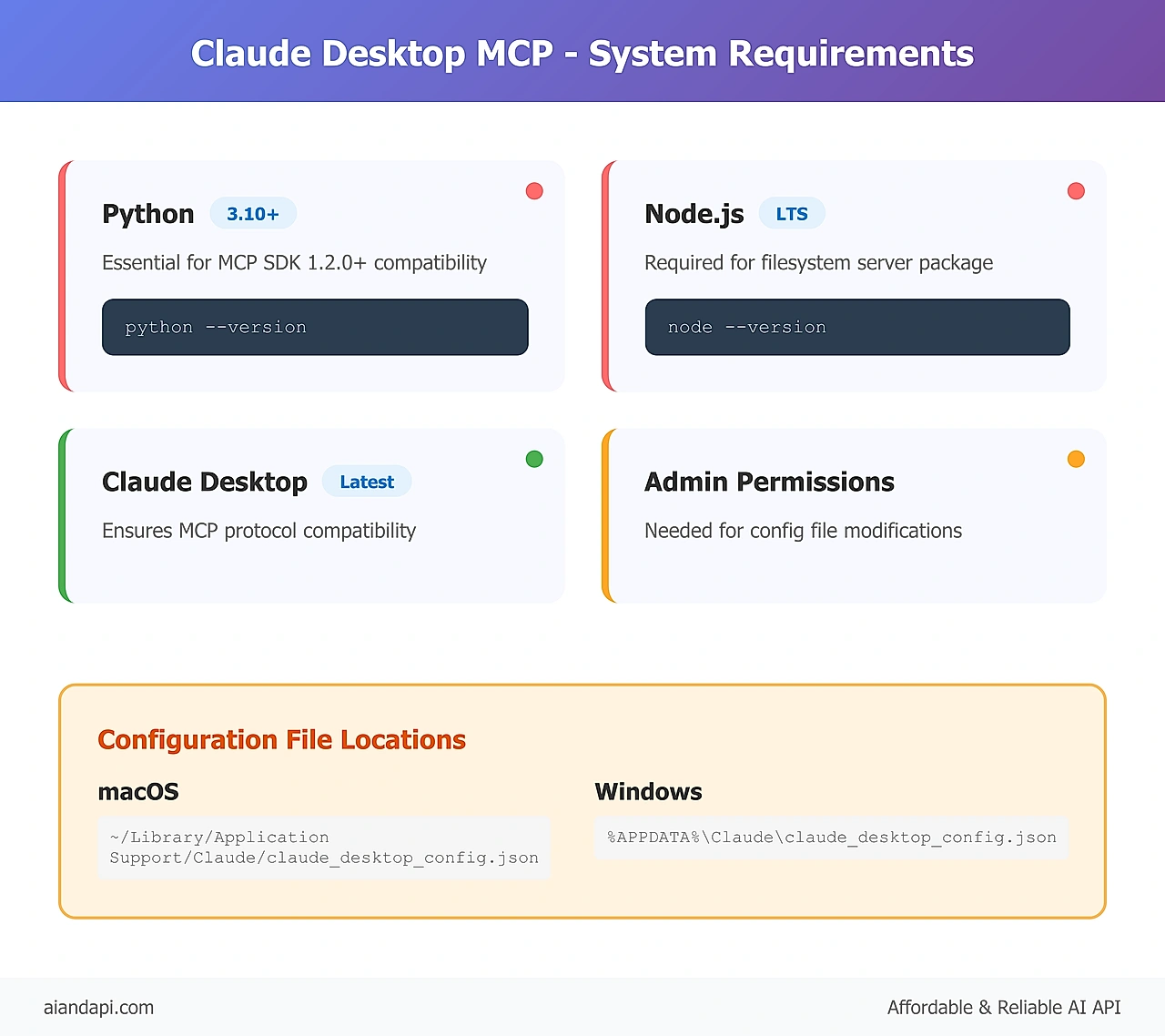
Before setting up MCP servers, make sure your system meets the official requirements. According to the MCP Quickstart Guide 2025 (authority source), you need Python 3.10 or higher for most MCP server development and execution. You'll also need Node.js LTS version for popular servers like the filesystem server.
Your Claude Desktop application must be running the latest version to support MCP functionality. The protocol is currently in beta status, as noted in official Anthropic documentation, which means features and requirements may evolve with updates.
Critical Claude Desktop MCP System Requirements:
- Python 3.10+ - Essential for MCP SDK 1.2.0+ compatibility (authority source: MCP Quickstart Guide)
- Node.js LTS - Required for @modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem package
- Claude Desktop latest version - Ensures Claude Desktop MCP protocol compatibility
- Administrative permissions - Needed for Claude Desktop MCP configuration file modifications
- JSON configuration skills - Basic understanding of Claude Desktop MCP config file format
Software Requirements Checklist
Verify each requirement before proceeding with MCP configuration:
- Python Installation: Run
python --versionto confirm Python 3.10 or higher - Node.js Setup: Execute
node --versionto verify LTS version installation - NPM Access: Confirm
npm --versionworks for package installation - Claude Desktop Update: Check for the latest version in your application settings
- Directory Permissions: Ensure write access to Claude Desktop configuration directories
Operating System Specific Notes
macOS Users: Configuration files are stored in ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json. You may need to create this file if it doesn't exist.
Windows Users: The configuration path is %APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json. Be aware of potential ENOENT errors with environment variable expansion, which require explicit path configuration in your JSON setup.
Step-by-Step Claude Desktop MCP Setup Process
Setting up Claude Desktop MCP servers follows a systematic 6-step process that ensures proper configuration and functionality. This how to setup Claude Desktop MCP guide provides the complete workflow from initial setup to verification.
How to Setup Claude Desktop MCP - 6 Essential Steps:
- Locate Configuration File - Find your configuration file at
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json(macOS) or%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json(Windows) - Install Required Dependencies - Install Node.js LTS and Python 3.10+ for compatibility
- Configure MCP Server - Add server configuration in JSON format with proper syntax
- Restart Claude Desktop - Perform complete application restart to load new settings
- Verify MCP Connection - Look for server indicators in Claude Desktop interface
- Test Server Functionality - Execute sample commands to confirm server operation
Authority Source: Based on Connect to Local MCP Servers official documentation and MCP Quickstart Guide requirements.
Detailed Setup Instructions
Step 1: Configuration File Location
Navigate to your operating system's Claude Desktop configuration directory. On macOS, this is ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json. On Windows, use %APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json. Create the file if it doesn't exist.
Step 2: Dependency Verification
Confirm Node.js installation with node --version and Python availability with python --version. These dependencies are essential for running popular MCP servers like the filesystem server.
Step 3: JSON Configuration Add your MCP server configuration to the JSON file using the official format. The basic structure includes an "mcpServers" object containing your server definitions with commands and arguments.
Step 4: Application Restart Completely quit and restart Claude Desktop to load the new configuration. This step is critical as configuration changes only take effect after a full application restart.
Step 5: Connection Verification Look for MCP server indicators in Claude Desktop's interface. Successfully connected servers appear in the application's status area or settings panel.
Step 6: Functionality Testing Test your MCP server by asking Claude to perform server-specific actions. For a filesystem server, try asking Claude to list directory contents or read a specific file.
Configuration Examples and Best Practices
Implementing MCP servers requires precise JSON configuration following official standards. Here are proven configuration examples based on Connect to Local MCP Servers documentation and MCP Quickstart Guide specifications.
Basic Filesystem Server Configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"/Users/username/Desktop",
"/Users/username/Downloads"
]
}
}
}
This configuration enables Claude Desktop to access specified directories for file reading, creation, and management. The filesystem server is one of the most popular MCP implementations, providing comprehensive file system integration capabilities.
Weather Server Configuration Example:
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/FOLDER/weather",
"run",
"weather.py"
]
}
}
}

Filesystem Server Configuration Template
The filesystem server requires absolute paths for security and reliability. Specify only directories you want Claude to access, following the principle of least privilege. Each directory listed in the args array becomes accessible to Claude for reading, writing, and file management operations.
Security considerations:
- Only grant access to directories you're comfortable with Claude modifying
- Use absolute paths to prevent confusion and security issues
- Regularly review configured directories and remove unused access
Security and Permission Best Practices
MCP server security follows an explicit approval model where all actions require user consent before execution. However, proper configuration reduces security risks:
- Directory Scope Limitation: Restrict filesystem server access to specific, necessary directories
- Regular Permission Auditing: Periodically review and update server configurations
- Official Server Priority: Prefer official MCP servers over third-party implementations
- Environment Variable Security: Avoid storing sensitive data in configuration files
Testing and Verification Methods
Verifying successful MCP setup requires systematic testing of connection status and server functionality. This Claude Desktop MCP quickstart verification ensures your configuration works correctly before production use.
Claude Desktop MCP Connection Verification Steps:
- Visual Indicator Check: Look for server status indicators in Claude Desktop interface
- Server Listing Confirmation: Ask Claude to list available servers and tools
- Basic Functionality Test: Execute simple server-specific commands
- Error Log Review: Check logs for connection or execution errors
- Independent Server Testing: Test servers outside Claude integration
- Permission Validation: Confirm server permissions and access rights
Visual Connection Indicators
Claude Desktop displays MCP connection status through interface indicators. Successfully connected servers show up in the application's settings or status area. Missing indicators usually point to configuration errors or server connection failures.
Functional Testing Commands
Test MCP server functionality with these verification commands:
Filesystem Server Testing:
- "Can you list the contents of my Desktop directory?"
- "Please read the contents of [specific file name]"
- "Create a new file called test.txt in my Downloads folder"
Generic Server Testing:
- "What MCP servers are currently connected?"
- "Show me the tools available from [server name]"
- "Can you use [server name] to [specific function]?"
Keep an eye on these commands for proper execution and expected responses to confirm your MCP setup is working as intended.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Solutions
MCP setup can run into several predictable issues with well-established solutions. This Claude Desktop MCP troubleshooting guide addresses the most frequent problems based on official documentation and community experience. For comprehensive error resolution, check out our dedicated Claude Desktop MCP troubleshooting guide covering advanced debugging techniques and error scenarios.
Common MCP Setup Problems and Solutions:
- ENOENT Windows Path Errors - Add expanded path values to "env" key in configuration
- NPM Global Installation Issues - Install NPM globally:
npm install -g npm - Server Not Showing in Claude - Restart Claude Desktop, check JSON syntax, verify file paths
- Permission Denied Errors - Confirm directory access rights and absolute path usage
- Server Connection Timeouts - Test server independently before Claude integration
File Path and Permission Errors
Path configuration errors top the list of common MCP setup issues. Windows users often run into ENOENT errors when using environment variables like %APPDATA% in JSON configuration.
Solution for Windows ENOENT errors:
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [...],
"env": {
"APPDATA": "C:\\Users\\YourUsername\\AppData\\Roaming"
}
}
}
}
Always stick to absolute paths in MCP configurations to prevent path resolution issues across different operating systems and user environments.
Connection and Server Recognition Issues
If MCP servers aren't showing up in Claude Desktop, here's a systematic troubleshooting approach:
- Configuration Syntax Verification: Validate JSON formatting using online JSON validators
- Complete Application Restart: Quit Claude Desktop entirely—not just closing the window
- Log File Analysis: Check
~/Library/Logs/Claude/mcp*.log(macOS) or%APPDATA%\Claude\logs(Windows) - Independent Server Testing: Run server commands outside Claude Desktop to verify functionality
- Dependency Confirmation: Ensure all required packages and versions are properly installed
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How to configure MCP servers in Claude Desktop?
A: Configure Claude Desktop MCP servers by editing the claude_desktop_config.json file with proper JSON syntax, including server commands, arguments, and paths. Remember to restart Claude Desktop after making configuration changes to load your new settings.
Q2: Where is the Claude Desktop config file?
A: The Claude Desktop MCP configuration file lives at ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json on macOS and %APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json on Windows.
Q3: What is the correct JSON format for MCP?
A: Claude Desktop MCP configuration uses the mcpServers object format with server names as keys, containing command and args arrays for each server implementation.
Q4: How to verify MCP is working?
A: Verify Claude Desktop MCP functionality by checking interface indicators, asking Claude to list connected servers, and testing server-specific commands like file operations.
Q5: What is MCP in Claude Desktop?
A: Claude Desktop MCP (Model Context Protocol) lets Claude connect with local programs and data sources, expanding capabilities beyond text generation to include file management and custom integrations.
Q6: What are the prerequisites for MCP?
A: Claude Desktop MCP needs Python 3.10+, Node.js LTS, the latest Claude Desktop version, and proper system permissions for configuration file access.
Q7: Is MCP difficult to set up?
A: Claude Desktop MCP setup follows a straightforward 6-step process with clear documentation, though some basic technical knowledge helps with JSON configuration and dependency management.
Q8: What can MCP do with Claude Desktop?
A: Claude Desktop MCP unlocks file system access, API integrations, custom tool functionality, database connections, and specialized workflow automation.
Q9: Why is my MCP server not connecting?
A: Common Claude Desktop MCP troubleshooting steps include checking JSON syntax, verifying file paths, confirming dependencies, reviewing log files, and making sure you've done a complete application restart.
Q10: How to fix Claude Desktop MCP errors?
A: Fix Claude Desktop MCP errors by validating configuration syntax, using absolute paths, checking system permissions, and examining MCP log files for specific error messages.
Q11: What are common MCP setup problems?
A: Common Claude Desktop MCP issues include ENOENT path errors, npm installation problems, server recognition failures, and JSON configuration syntax mistakes.
Q12: How to debug MCP connection issues?
A: Debug Claude Desktop MCP connections by testing servers independently, reviewing log files, confirming dependencies, and validating configuration file syntax.
Next Steps and Advanced Usage
Mastering Claude Desktop MCP opens up tremendous possibilities for AI-enhanced productivity and workflow automation. This comprehensive Claude Desktop MCP tutorial has given you the foundation for successful MCP integration, from basic setup through advanced troubleshooting.
The key takeaways from this Claude Desktop MCP beginner guide include understanding core protocol functionality, implementing secure configuration practices, and maintaining reliable server connections. By following the official requirements of Python 3.10+, Node.js LTS, and proper JSON configuration formatting, you've established a robust foundation for MCP usage.
Advanced Claude Desktop MCP Development Opportunities:
- Custom API Integrations: Build MCP servers for specialized APIs
- Database Connectivity: Create servers for SQL and NoSQL databases
- Workflow Automation: Develop tools for business process automation
- Enterprise Integration: Implement solutions for team collaboration
- Security Enhancement: Advanced permission and audit systems
Your next steps should focus on exploring advanced server implementations through the official MCP GitHub repository which offers extensive resources for developing custom servers tailored to your specific use cases.
Consider joining the community through the official MCP Discord to stay updated on new server releases, share configuration experiences, and contribute to the growing ecosystem of Claude Desktop integrations. You can also explore our Claude Desktop API integration tutorials for advanced automation workflows. With MCP's beta status continuing to evolve, early adoption positions you at the forefront of AI-powered desktop computing innovation.
Authority Sources Referenced:
- Connect to Local MCP Servers Documentation (modelcontextprotocol.io)
- MCP Quickstart Guide 2025 (Official)
- Anthropic Help Documentation (support.anthropic.com)
- MCP GitHub Servers Repository (Official)